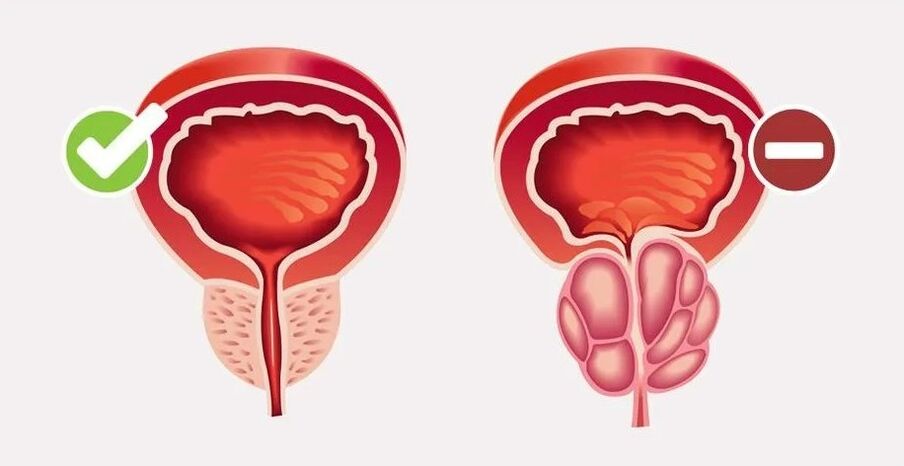
Prostatitis is an inflammation of male prostate tissue, which manifests as pain in lower abdomen and urination diseases. The disease is carried out in acute and chronic forms and develops under the influence of infectious and non-communicable causes. Prostatitis includes five of the most common questions for men to turn to a urologist.
The prostate is an organ of the male reproductive system, which produces liquid secrets, which are part of the sperm and improves sperm mobility. The prostate has the shape of a chestnut and measures 2x3x3. 5 cm and is located in the middle of the pelvic cavity. The initial part of the bladder's neck and urethra passes through the center of the gland.
Acute prostatitis is very rare (5-10% of cases), but the process is difficult and is a serious danger to men's health. Most young people suffer from acute inflammatory forms. Chronic prostatitis develops in men aged 60-70. The disease takes place with moderately obvious symptoms, but over time, the disease can lead to erectile dysfunction and impaired urination.
Causes and risk factors of prostatitis in men
All causes of prostatitis in men can be divided into two groups - infectious and non-infectious.
Acute inflammation of the prostateIt is contagious in most cases, and this disease is particularly common in men under the age of 40. In most cases, it is caused by bacterial flora:
- Enterococcus;
- E. coli;
- Klebsiella and proteases;
- gonococci;
- pale caterpillar;
- Chlamydia;
- Mycobacterium of tuberculosis.
However, in 100% of cases, urogenital or intestinal infections themselves can cause inflammation of the prostate. In order to develop bacterial prostatitis, inducing factors are needed, which are mainly microspots of the glands. This occurs during a prostate biopsy, cystoscopy, or surgery in the pelvis. Other risk factors for infectious prostatitis include:
- Immune deficit (HIV infection, innate pathology of the immune system);
- Random sex life;
- homosexual contact;
- Chronic diarrhea or constipation;
- obesity;
- A sedentary lifestyle.
The pathogenic microorganism penetrates the prostate from the urethra or rectum. Prostate immune protection and attenuation of microorganisms contribute to the development of acute inflammation. In this context, the tone of the smooth muscle of the prostate is elevated, which leads to compression of the urethra and urination disorders.
Chronic prostatitisIt has non-communicable origins and more complex development mechanisms. The inflammation gradually forms, and the exact cause of its occurrence has not been determined. Risk factors for chronic nonbacterial prostatitis:
- Increased pressure on the prostate gland (benign hyperplasia or adenoma);
- Increased pressure in the pelvic cavity;
- Chronic pelvic pain;
- autoimmune diseases;
- Rare sexual contact;
- Focus on physical exercise;
- Chronic stress.
The pathogenesis of chronic prostatitis is based on the secret stagnation of the glands, which deteriorates its blood supply, resulting in persistent inflammation.
In about 6% of cases, men develop chronic bacterial prostatitis. The reason is insufficient or incomplete treatment of acute forms of the disease.
Types of prostatitis
According to the reasons and mechanism of development, four clinicalForm of prostatitis:
- Acute bacteria;
- Chronic bacteria;
- Chronic nonbacterial (chronic pelvic pain syndrome);
- Asymptomatic inflammation.
The National Institutes of Health distinguishes 4 types of prostatitisFrom the development stage and the clinic:
- Type I - Acute bacterial inflammation with general and local manifestations;
- Type II - Period of chronic bacterial inflammation, recovery and aggravation;
- Type IIIA - Chronic nonbacterial (pathogenic microorganisms have not been detected) inflammation confirmed by the presence of white blood cells in the secret of prostate or ejaculation;
- Type IIIV - Non-inflammatory prostatitis, in which the secrets of the glands are free of pathogenic microorganisms and leukocytes;
- Type IV - Asymptomatic inflammation, only confirmed histologically.
depending onFrom the nature of pathological processesIn the prostate, they distinguish:
- Kata's prostatitis - Acute simple inflammation;
- Stagnant or congestive prostatitis - Chronic inflammation is associated with obstruction of gland ducts and the accumulation of secrets in the prostate;
- Calculate prostatitis - a chronic form of disease complications accompanied by stone formation in the glandular duct;
- Granular prostatitis is an extremely rare form accompanied by thickening of the mucosal membrane of the glandular duct.
Symptoms of prostatitis in men
Clinical images of prostatitis in men include signs of prostatitis, compression of the bladder neck and urethra, and general manifestations of the disease. The severity and combination of symptoms depends on the shape and stage of prostatitis.
Common performanceDiseases, regardless of their form, can be used:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, tailbone and ac bones;
- Violation of urination with rapid impulse, discomfort and burning, intermittent flow;
- Violation of effectiveness and ejaculation.
The acute form of prostatitis begins suddenly and takes place with obvious symptoms, usually with various complications. Chronic inflammation gradually develops, characterized by periods of aggravation and relief. For bacterial prostatitis, first of all, the sign of symptoms (fever, nausea), the noninfectious form of the disease, local inflammation of the prostate is the main importance.
Signs of acute prostatitis
With acute bacterial inflammation in the prostate, men experience the following symptoms:
- Generally discomfort;
- Fever exceeds 38°C;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen, rectal radiation;
- Frequent, but difficult to urinate at the same time;
- itching and burning in the urethra;
- The shadow of urine, the appearance of blood or pus.
In the future, various consequences will occur in the treatment background or in the chronic form of bacterial prostatitis.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis
When chronic bacterial prostatitis develops after acute inflammation, a person is worried about periodic pain in the lower abdomen, difficulty urinating, and sometimes burning in the urethra. The pain can also spread to the lower back and tailbone, rectum, penis, and scrotum. Symptoms usually occur during aggravated prostatitis, and during remission, the human well remains normal.
Non-infected prostatitis in men is also known as chronic pelvic pain, which includes pain and signs of urination and sexual illness. It is difficult for a person to urinate because the urine flows slowly and intermittently, and the urethra and the stress sensation are burning. As the disease progresses for a long time, ejaculation becomes inferior and painful. In the end, a person's quality of life suffers a huge impact and psychological problems will arise.
Prostatitis pain
Pain syndrome of prostatitis is a constant and most obvious symptom that is present in all forms of disease. The mechanisms of prostatitis pain are caused by inflammation and edema of the glands, compression of the bladder neck receptor, and the initial part of the urethra.
The acute form of the disease is accompanied by the most severe pain, because the inflammation is infectious, causing a lot of edema in the glands. The pain is located in the prostate itself, but the man feels it not only in the lower abdomen, but also in the lower back, core, rectum, and scrotum.
With chronic inflammation of the prostate, pain is painful, but longer in nature, it may not disappear even during remission. Syndrome of chronic pelvic pain is accompanied by the prostate itself as well as the tailbone itself at the base of the anus, penis and scrotum as well as the tailbone. Discomfort bothers men at least three months a day.
More dangerous than prostatitis
Complications include both acute and chronic forms of prostatitis:
- Vesicles (inflammation of seed bubbles);
- Glycite (inflammation of seed nodules);
- prostate abscess (abscess in capsule);
- prostate fibrosis (forming scars in gland tissue);
- cysts in the prostate;
- prostate;
- Infertility due to deterioration in sperm mass;
- Erectile dysfunction caused by chronic pelvic pain and mental illness;
- Frustrated.
Diagnosing inflammation of prostatitis
When the first sign of prostatitis appears, you need to contact your urologist. First, the doctor talks with the patient to determine the nature of the complaint and collect anatomy. To do this, the doctor asked the following questions:
- How long have the symptoms of the disease been present?
- Where the pain is local, its characteristics and conditions of occurrence;
- There are any problems with urination and ejaculation;
- Are there any chronic diseases, including urogenital infections.
To diagnose prostatitis, doctors use the following methods:
- Rectal examination of the fingers of the prostate;
- General clinical blood tests;
- Bacteriological examination of ejaculation or prostate secretion;
- Ultrasound examination of pelvic organs;
- Urinary method;
- Radiography or computed tomography of the prostate;
- In rare cases, a biopsy of the prostate may be required and then a histological examination is performed.
Treatment of prostatitis in men
To treat male prostatitis, conservative methods are mainly used, and tactics depend on the cause and stage of the disease development. Asymptomatic inflammation (type IV) does not require active treatment. Among other forms of disease, complicated treatments are shown, and the acute form of prostatitis requires hospitalization in the hospital, which can treat chronic inflammation in the outpatient clinic.
First of all, the doctor recommendsLifestyle correction:
- Refuse to smoke and drink;
- Regular sex life;
- Remove pressure;
- Enough physical exercise;
- Balanced diet;
- Excluding hypothermia and overheating.
The prerequisite for successful treatment of prostatitis isEliminate related diseases, especially urogenital infections.
Drug TherapyUse prostatitis, which is designed to suppress the inflammatory process, improve urination and relieve pain. Use the following drug groups:
- antibiotic. Through acute bacterial inflammation, doctors have prescribed the results of microbial examinations of the prostate secretly by drugs. Oral medications can be taken in the form of tablets or in the form of intramuscular injection. The treatment process is usually 4-6 weeks, acute form of the disease. In chronic bacterial prostatitis, the duration of treatment is determined separately.
- alpha receptor blocker. These medications are designed to improve urination as they relax the smooth muscles of the glands and eliminate compression in the urethral prostate. In chronic forms of disease, they have to last for a long time, sometimes even life.
- musorelaxants and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are shown to eliminate pain syndromes caused by inflammation of their muscles and muscle spasms.
- Among chronic inflammation, drugs used to improve microcirculation, immunomodulators, antidepressants, and drugs used to stimulate erections are pointed out.
Acute inflammation of the prostate can be treated with medication and in most cases, it will fully recover within 1. 5-2 months. In the chronic form of the disease, treatment lasts for a long time or life.
An important method for treating congestive prostatitis is to massage the prostate through rectal renal massage. The procedure is done by a urologist in the clinic. Massage helps remove muscle cramps and stimulates the release of secrets of the prostate.
Physical Therapy ProceduresIn the chronic course of prostatitis, it is shown:
- laser therapy;
- Electrophoresis and superbuoyancy;
- microwave therapy;
- Electrical stimulation;
- acupuncture.
Surgical interventionShown only as complications develop - abscess or prostate stones.
Predict and prevent
The prognosis of recovery of acute bacterial prostatitis is timely and complex treatment. A chronic form of transition was observed in 6-10% of cases. Usually, chronic nonbacterial prostatitis cannot be completely cured. Complex treatments allow you to slow the progression of the disease, preserve the person’s quality of life and reduce the risk of complications.
Preventing the development of prostatitis in men includes the following suggestions:
- A healthy lifestyle;
- Regulate work and rest regimes;
- Balanced diet and drinking patterns;
- Enough physical exercise;
- Regular sex (ejaculation);
- Prevent reproductive infections;
- Limitations of invasive manipulation (cystoscopy, urethral catheterization, prostate biopsy);
- Prevent genital damage.













